IUPAC classification of elements
IUPAC classified the elements serially from 1 to 18. The classification of elements in the modern periodic table in the period from 1 to 7 and group from 1 to 18 is the IUPAC classification of elements.
Nuclear charge
The nucleus consists of proton and neutrons where the neutron is neutral and a proton has a positive charge. So, the total charge on the neutron is called the nuclear charge.
Effective nuclear charge
The nucleus is centrally located and is positively charged. Electrons are negatively charged and are distributed out of electrons. There exists an electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. The nuclear attraction felt by valence electron is called effective nuclear charge.
Periodicity in physical properties of elements
A. Atomic Radius
It is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell having an electron.
Variation of atomic radius in a period: On moving from left to right in a period, nuclear charge increases. Therefore the electrons are attracted more strongly by the nucleus due to which the size of the atom decreases.
Variation of atomic radius in a group: On moving from top to bottom in a group, the number of shells increases due to which the size of the atom increases.
B. Ionic radius
It is defined as the effective distance between the centre of the nucleus and a point up to which the nucleus has its influence on its electron in an Ion.
By the study of Ionic radius, following conclusions are made:
i. A cation is smaller than its parent atom: Cation is formed by the removal of one or more electron from its neutral atom. It means a cation has a less number of electrons than the parent atom. Therefore, effective nuclear charge increases in cation and are more strongly pulled by the nucleus in the parent atom due to which the size of cation decreases.
Na>Na+ Ca>Ca++
ii. An anion is larger than its parent atom:
An anion is formed by the addition of one or more electrons to the neutral atom. It means an anion has more electrons than its parent atom. Therefore effective nuclear charge decreases in an anion and is less strongly pulled by the nucleus than in the parent atom due to which the size of anion increases.
Cl<Cl– O<O– –
iii. Size of cation decreases with the increase in positive charge on the cation:
This is due to the increase in effective nuclear charge with an increase in positive charge on the cation.
Cr > Cr+ > Cr++ > Cr+++
iv. In isoelectric ion, ionic radius decreases with an increase in nuclear charge:
Ions having the same number of electrons but a different nuclear charge is called isoelectric ions. As the nuclear charge increase, electrons are more strongly attracted by the nucleus due to which size decreases.
N3- > O2- F– > Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+
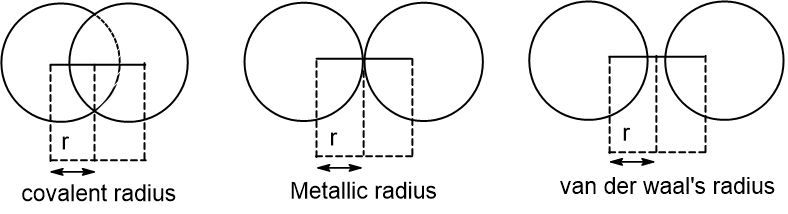
- Covalent radius is half of the distance between the two nuclei in a homonuclear diatomic molecule bonded by a single covalent bond.
- Metallic radius is half the distance between two nuclei of atoms held by a metallic bond.
- van der Waal’s radius is half the distance between two non bonded nuclei of atoms held by van der Waal’s force of attraction.
Ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is called ionization energy.
M(g) + IE → M+(g) + e–
Successive ionization energies:
The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is called first ionization energy.
M(g) + IE1 → M+(g) + e–
The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated gaseous mono positive cation is called second ionization energy.
M+(g) + IE2 → M++(g) + e–
The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated gaseous dipositive cation is called third ionization energy.
M++(g) + IE3 → M+++(g) + e–
For the same element, IE1<IE2<IE3
Factors affecting ionization energy
1. Atomic size: Ionization energy increases with decrease in size of atom.
2. Nuclear charge: Ionization energy increases with increase in nuclear charge of atom.
3. Electronic configuration: Half filled and completely filled orbitals are more stable than other configuration. More energy is required to remove an electron from a more stable orbital. So ionization energy is high to remove an electron from half filled and completely filled orbitals.
4. Screening for shielding effect: In the multi-electron atom, the electron lying between the nucleus and the valence shell (intervening electrons) shields the outermost electron from the nucleus. This effect of shielding of valence electron from the nucleus due to the intervening electron is called screening or shielding effect. Greater the number of the intervening electron, higher the shielding effect. So electrons are less strongly attracted by the nucleus and less energy is required to remove the electron. So ionization energy decreases with an increase in shielding effect.
5. Penetration effect: In a given shell, s electrons penetrate more toward the nucleus than corresponding p-electrons and so on. Therefore more energy is required to remove an electron from the s-orbital than the corresponding p-orbital and so on. So ionization energy of the orbital follows the order: s-orbital>p-orbital>d-orbital>f-orbital.


