Fertilizer
A fertilizer is a material that is added to the soil to provide nutrients to the plant and to promote healthy growth.
Qualities of good fertilizer are:
- Freely soluble in water
- Should not undergo chemical change with time.
- Should be cheap.
- Should not injure the host cell of plants.
Classification of fertilizer
- Natural or organic fertilizer:
They are obtained from dead and decayed plant and animal bodies. eg cow dung, animal bone powder, etc.
- Artificial or chemical fertilizer:
They are synthesized in the laboratory or industries. eg. Urea, ammonium sulphate, etc.
Nitrogen fertilizer: They supply nitrogen to the plants. eg. urea (NH2CONH2), ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3), calcium ammonium nitrate(CAN), etc. They help in rapid growth, increase yield, and increase protein content.
Phosphatic fertilizer: They supply phosphorous to the plant. They are used in the development of roots. eg. Thomas slag (Ca3(PO4)), calcium superphosphate (CaH4(PO4)2), etc.
Potash fertilizer: They supply potassium to the plant. eg. Sylvine (KCl), niter (KNO3), K2SO4, K2CO3, etc. They are required for the growth of carbohydrates.
Simple and mixed fertilizer: A fertilizer containing one primary nutrient is called simple fertilizer. eg. urea, ammonium sulphate, potassium chloride, etc. A fertilizer containing two or more primary nutrients is called mixed fertilizer. eg. potassium nitrate (KNO3), ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4, Calcium ammonium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2+NH4NO3), etc.
Production of urea
Urea is also called carbamide which is a colourless organic compound soluble in water.
The raw materials used for the production of urea are liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. Ammonia is manufactured by Haber’s process and CO2 by the decomposition of CaCO3. The chemical reaction takes place as:
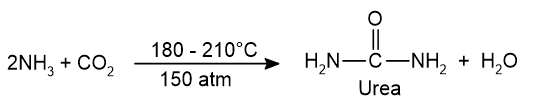
Steps:
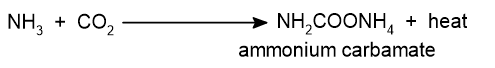
i. Formation of ammonium carbamate: Ammonia and carbon dioxide react under high temperatures and high pressure to form ammonium carbamate.
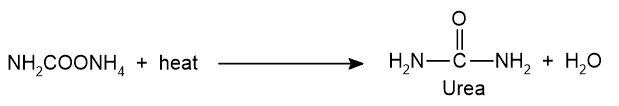
ii. Decomposition of ammonium carbamate: Ammonium carbamate is decomposed to urea.
Some Important Questions
- Define applied chemistry. What are the challenges in establishing chemical industries in a country like Nepal?
- Distinguish between continuous and batch processing systems.
- How does air pollution occur due to the chemical industry?
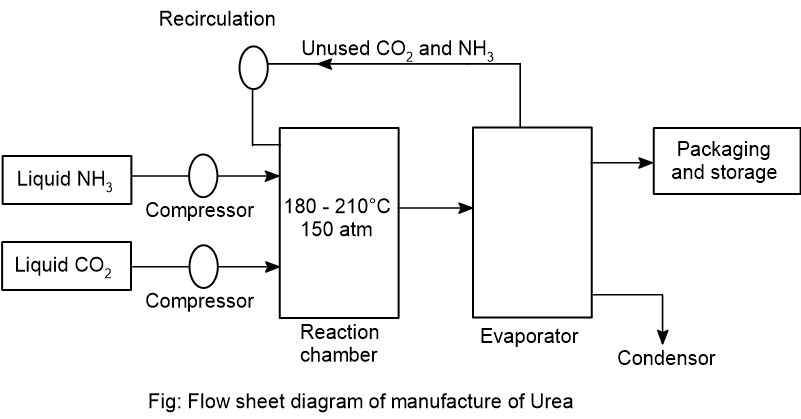
- Write the principle and flow sheet diagram for the manufacture of urea.


