Some of the derivatives of carboxylic acid are acid halide, acid amide, ester, acid anhydride.
A. Acid halides (R-COCl):
Nomenclature (IUPAC name- Alkanoyl chloride):

Preparation:
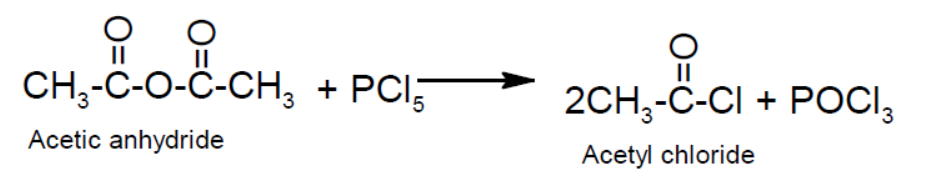
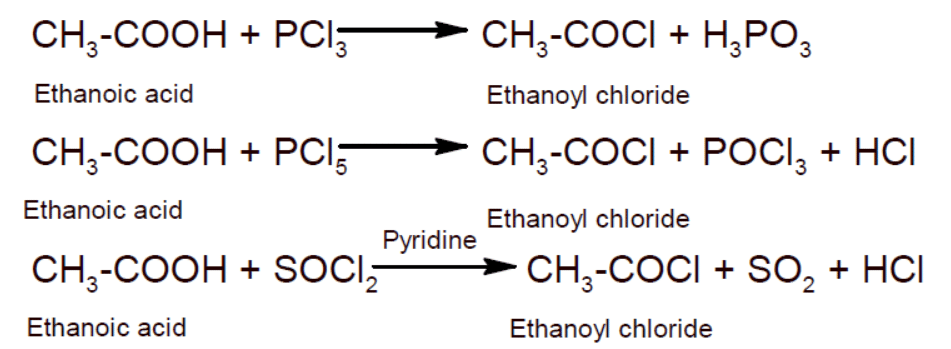
- From carboxylic acid: Carboxylic acid reacts with PCl3, PCl5 or SOCl2 to give acid chloride.
Physical Properties:
- Lower members are colorless liquids having irritating odour and higher members are colorless solid.
- Acid chlorides are insoluble in water due to a lack of intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water.
- The boiling point of acid chloride is less than parent acid due to the absence of hydrogen bonding. Formyl chloride (HCOCl) is unstable.
Chemical Properties:
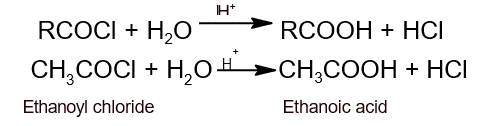
- Action with air:
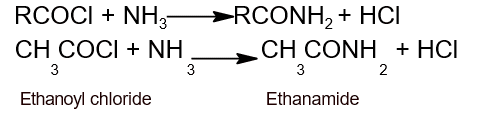
- Action with ammonia
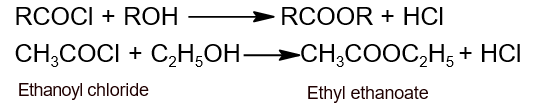
- Action with alcohol:
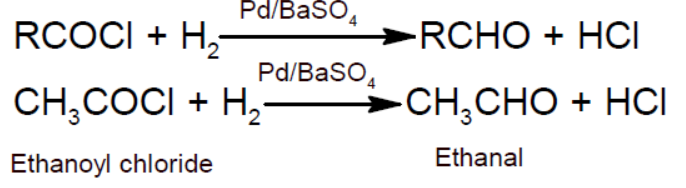
- Rosenmund reaction:
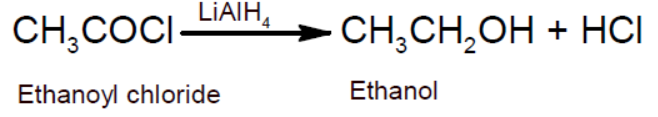
- Reduction to alcohol:
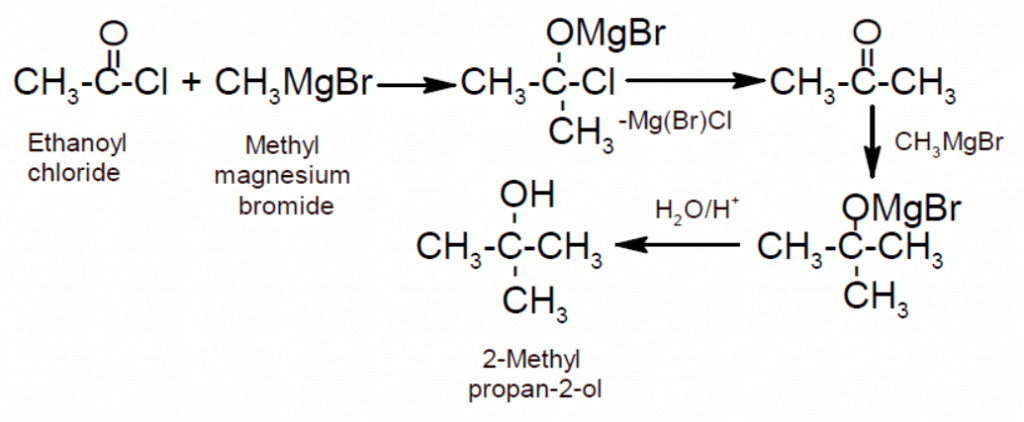
- Action with Grignard’s reagent:
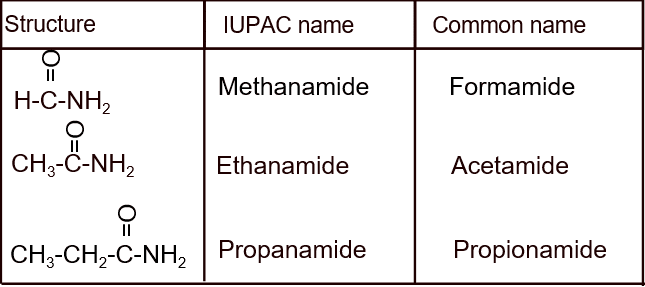
B. Acid Amide (R-CONH2):
Nomenclature (IUPAC name- Alkanamide):
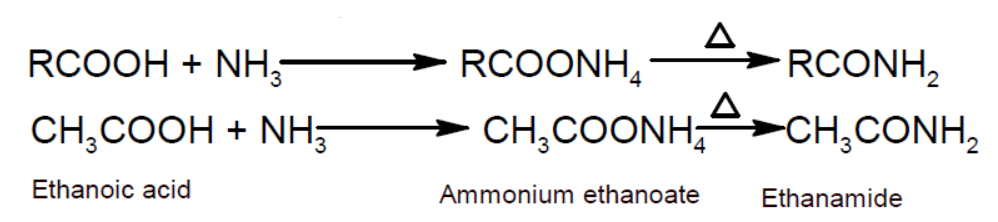
Preparation:
- From carboxylic acid:
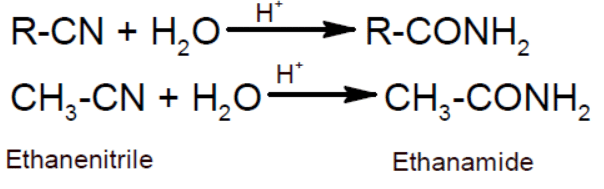
- From partial hydrolysis of alkanenitrile:
Physical Properties:
- Almost all amides are colorless, odourless, and crystalline solid. Formamide is a liquid.
- Lower members are soluble in water due to hydrogen bond formation.
- They have a higher boiling point than corresponding acids.
Chemical Properties:
- Amphoteric Nature:
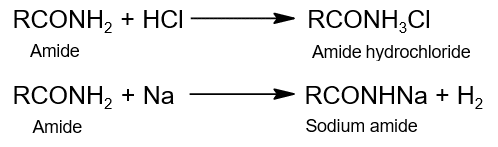
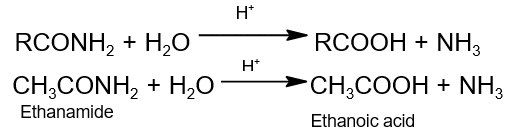
- Hydrolysis:
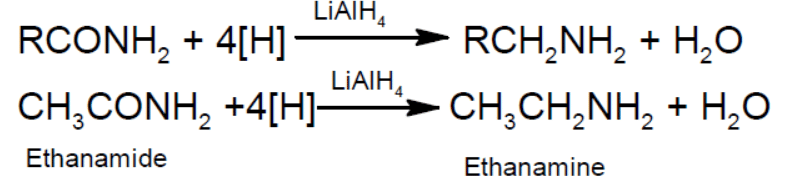
- Reduction:
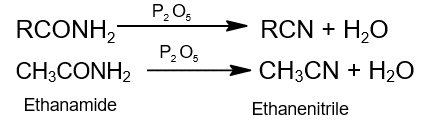
- Dehydration:
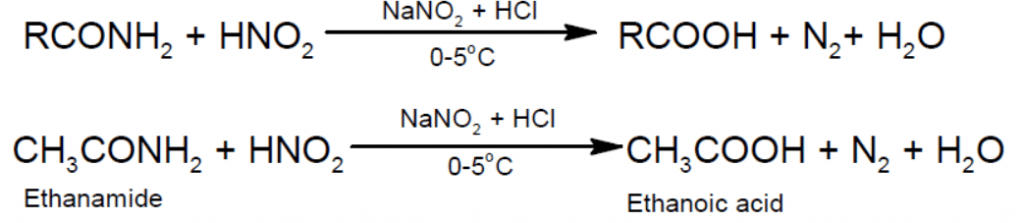
- Action with nitrous acid:
- Hoffman Hypobromide reaction (decarbonylation):
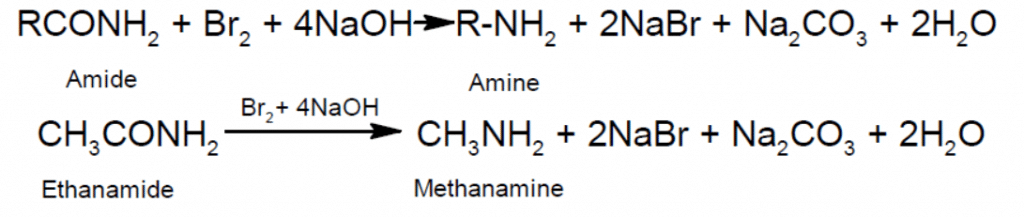
C. Ester (RCOOR):
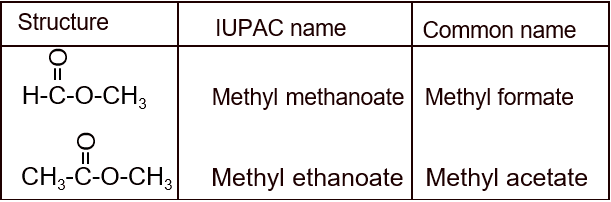
Nomenclature (IUPAC name- Alkyl alkanoate):
Preparation:
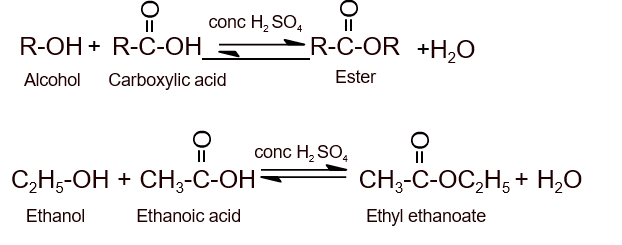
- From carboxylic acid (Esterification):
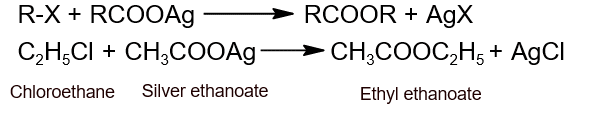
- From haloalkane:
Physical Properties:
- Esters are colorless oily liquids with a fruity odour.
- They are sparingly soluble in water.
- The boiling points of esters are always less than corresponding carboxylic acids.
Chemical Properties:
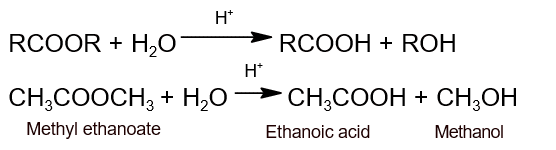
- Hydrolysis:
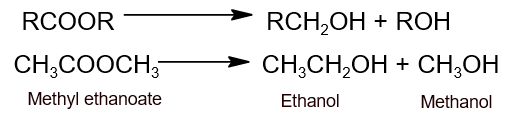
- Reduction:
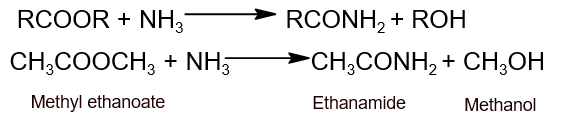
- Ammonolysis:
- Action with PCl5:

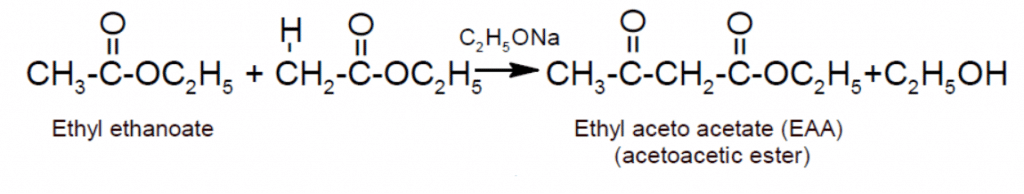
- Claisen condensation: Esters having -hydrogen reacts with a base like sodium ethoxide to form ethyl acetoacetate (EAA).
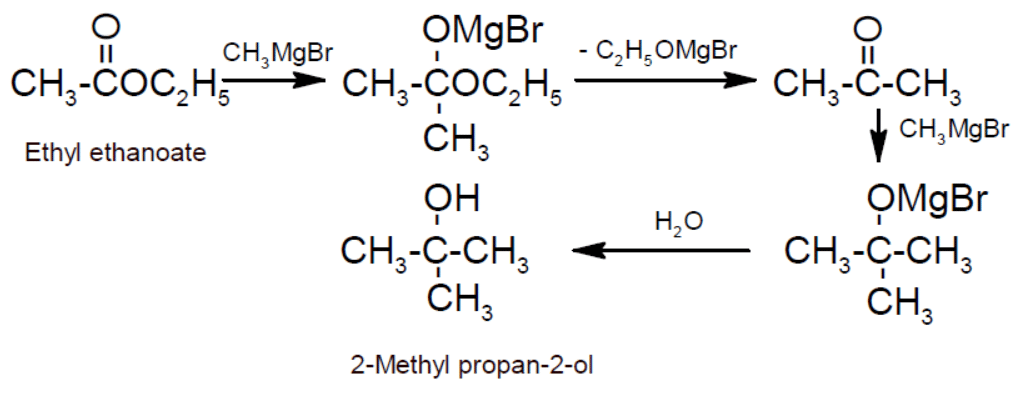
- Action with Grignard’s reagent:
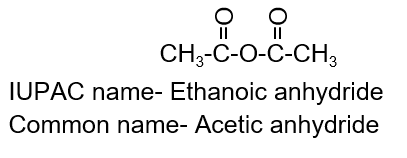
D. Acid anhydride:
Nomenclature (IUPAC name- Alkanoic anhydride):
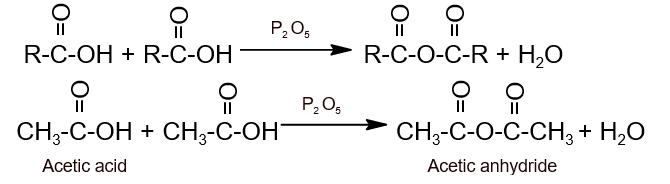
Preparation:
- From carboxylic acid:
Physical Properties:
- Lower members are colorless liquid having a sharp irritating smell. Higher members are colorless solids.
- Lower members are soluble in water.
- They have a higher boiling point than parent carboxylic acid.
Chemical Properties:
- Hydrolysis:
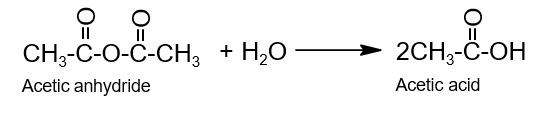
- Ammonolysis:
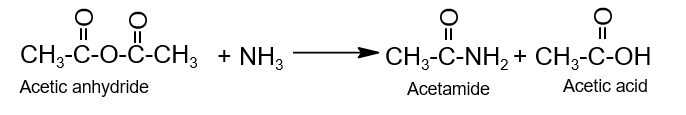
- Alcoholysis:
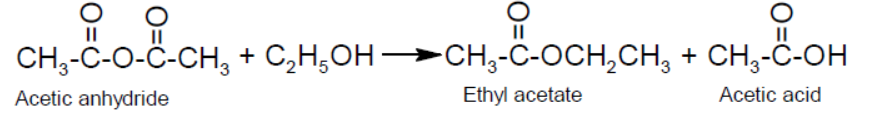
- Reduction:
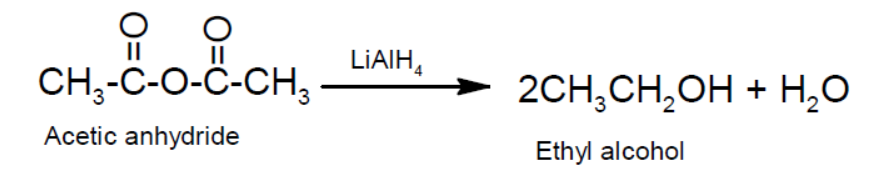
- Action with PCl5