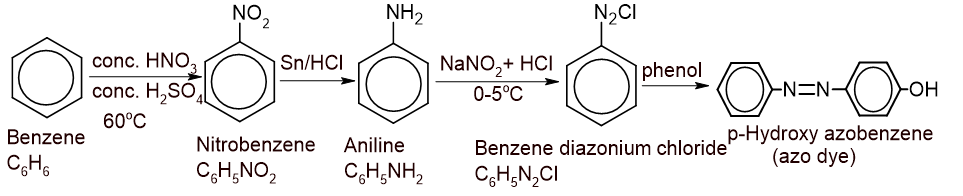
6. A list of compounds are given as follows:
| p-hydroxyazobenzene, C6H5N2Cl, C6H5NH2, C6H5NO2, C6H6 |
From the above list of compounds, prepare a sequence of reaction chains with suitable conditions and reactions. (1+1+1+1+1)
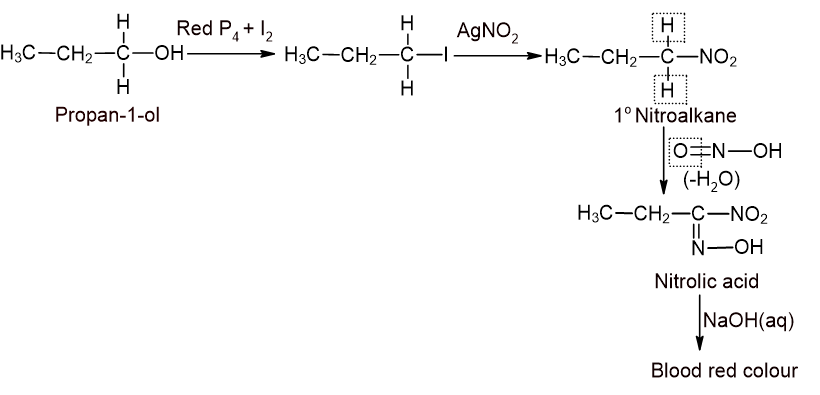
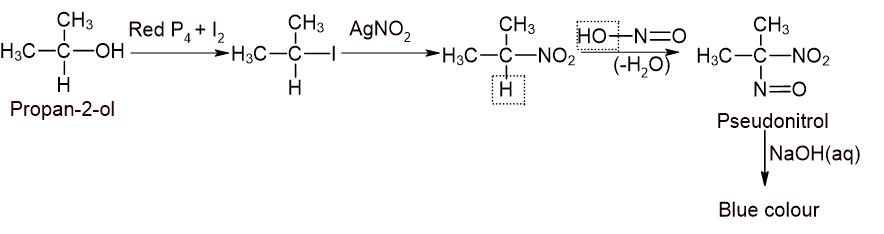
7. Write down the isomeric alcohols of C3H8O and their IUPAC name. How would you apply Victor Meyer’s test to distinguish these isomers? (2+3)
Ans:
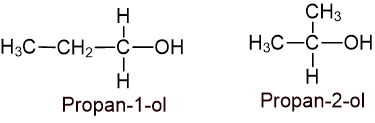
Distinction:
- Given alcohol is treated with PI3 (red P4 + I2) to get corresponding Iodoalkane.
- The iodoalkane thus formed is treated with alcoholic AgNO2 solution to get corresponding nitroalkane.
- The nitroalkane thus formed is treated with nitrous acid(HNO2) and then with aqueous alkali.
-If blood red colour is formed, the alcohol is primary.
-If blue colour is formed, the alcohol is secondary.
For 1° alcohol
For 2° alcohol
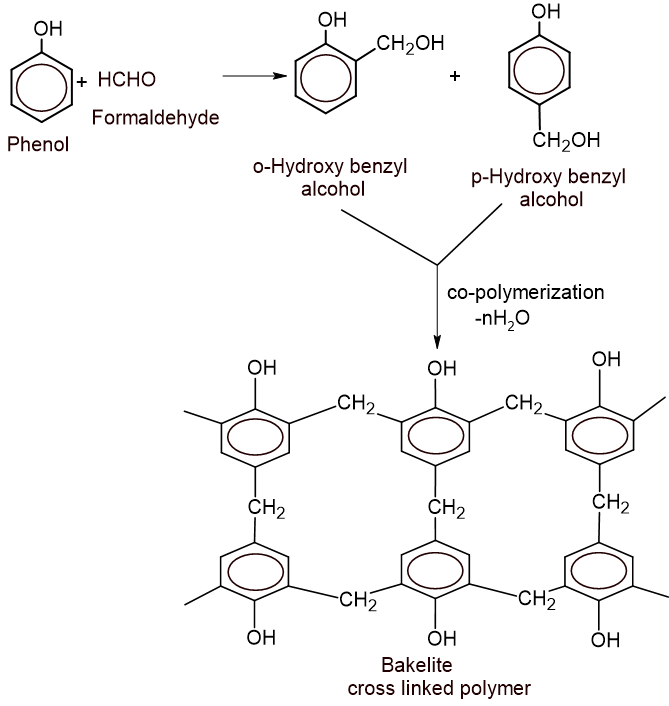
8. A) Define condensation polymerization. Write the molecular structures of monomers of Bakelite. (1+2)
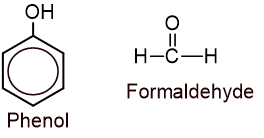
Ans: A polymer formed by the addition of monomers with the elimination of smaller molecules like water is called condensation polymer. eg. nylon-6,6, bakelite, etc.
Monomers of bakelite: Phenol and formaldehyde
B) Differentiate between OPC and PPC cement. (2)
Ans:
| Ordinary Portland Cement(OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| Manufactured by grinding a mixture of limestone and other raw materials like argillaceous, calcareous gypsum to a powder. | PPC is a variant of OPC. Pozzolana materials namely fly ash, volcanic ash are added to the OPC to produce PPC. |
| It is more expensive than PPC. | It is cheaper than OPC. |
| Less durable in aggressive weather. | More durable in aggressive weather. |
| Low resistance against alkali, sulphates and chlorides. | High resistance against alkali, sulphates and chlorides. |
Group C: Long Answer Questions (3 × 8 = 24)
9. (A) What amount of Zn(OH)2 will be precipitated out at 25°C if 100 ml of 0.22gm NaOH is added to 1 litre of a saturated solution of Zn(OH)2? Precipitate is obtained in this reaction, why? [solubility product of Zn(OH)2 at 25°C is 1.8 x 10-14]
Ans:
Number of moles of Zn(OH)2 precipitated = Number of moles of Zn(OH)2 dissolved initially – Number of moles of Zn(OH)2 dissolved after the addition of 100 ml of 0.22 gm NaOH
For Zn(OH)2, Zn(OH)2(s) ⇌ Zn++(s) + 2OH–(2s)
\begin{align*}K_{sp} = [Zn^{++}][OH^{-}]^{2} &= s.(2s)^{2} = 4s^{3}\\or,\ 1.8\times10^{-14}&=4s^{3}\\\therefore s=1.65\times &10^{-5}\ M\end{align*} When NaOH is added to Zn(OH)2 solution, then some Zn(OH)2 or Zn++ gets precipitated.
After dilution, the concentration of the solution is given by:
\begin{align*}initial\ conc.&\times \frac{intial\ vol.}{final\ vol.}\\=1.65\times &10^{-5}\times\frac{1000}{1100}\\=1.5\times &10^{-5}M\end{align*} So, concentration of Zn++ after mixing = 1.5 x 10-5 M.
One mole of Zn(OH)2 gives 2 moles of OH– ions,
For NaOH, 100 ml of 0.22 gm NaOH = final volume(1100 ml) x final concentration
\begin{align*}V_{1}N_{1}&=V_{2}N_{2}\\or,\ \not V_{1}\times\frac{w}{\not v}\times &\frac{1000}{eq.\ wt.}= 1100\times s\\or,\ 0.22\times \frac{1000}{40}&=1100\times s\\\therefore s&= 0.005M\\or,\ [OH^{-}]&=0.005M\end{align*} Total [OH–] = [OH–] from Zn(OH)2 + [OH–] from NaOH
= 2 x 1.65 x10-5 x (1000/1100) + 0.005
= 5.03 x 10-3M
But due to the addition of NaOH, Zn(OH)2 gets precipitated due to the common ion effect and the concentration of Zn++ is suppressed.
Ksp = [Zn++ dissolved] [OH–]2
\begin{align*}[Zn^{++}\ &dissolved]=\frac{K_{sp}}{[OH^{-}]^{2}}\\&=\frac{1.8\times 10^{-14}}{(0.008)^{2}}\\&= 7.11\times 10^{-10}M\\\left [ Zn^{++} \right ]\ precipitated &= [Zn^{++}]total-[Zn^{++}]dissolved\\&=1.5\times 10^{-5} - 7.11\times 10^{-10}\\&=1.49\times 10^{-5}mol/lit\end{align*} Since the ionic product is greater than the solubility product, the precipitate is formed.
(B) Potassium hydroxide having pH 8 is diluted 1000 times. Calculate the pH of the diluted base. (3)
Solution:
Here, pH = 8
or, [H+] = 10-8 M
since, [H+] [OH–] = 10-14]
so, [OH–] = 10-6 M
Since KOH is diluted 1000 times. So, its concentration will be decreased by 1000 times.
Molarity of diluted base = 10-6/1000 = 10-9M
If [OH–] = 10-9 then pOH =9, pH = 14-9 =5, which is incorrect.
Now,
\begin{align*}[OH^{-}]_{total}&=[OH^{-}]_{diluted\ KOH}+[OH^{-}]_{H_{2}O}\\&=10^{-9}+10^{-7}\\&=1.01\times 10^{-7}M\\We\ know&,\ pOH=-log[1.01\times 10^{-7}]\\&=6.995\\\therefore pH&=14-6.995=7.005\end{align*} OR
(A) Calculate the heat of formation of ethyl alcohol from the given data. (4)
| Heat of combustion of ethyl alcohol | -330 kcal |
| Heat of formation of Carbon dioxide | -94 kcal |
| Heat of formation of water | -68.5 kcal |
Solution:
C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(l), ΔH = -330 Kcal ………(i)
C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g), ΔH = -95 Kcal……(ii)
H2(g) + 1/2O2 H2O(l), ΔH = -68.5 Kcal……(iii)
2C(s) + 3H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) C2H5OH(l), ΔH = ?
(ii) x 2 + (iii) x 3 – (i)
2C(s) + 3H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) C2H5OH(l), ΔH = 63.5 Kcal
(B) The standard electrode potential for the following electrode reaction at the standard state is given.
Cu(s) → Cu++ (aq) + 2e–………E0 Cu++/Cu= +0.34V
Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) …………E0 Ag+/Ag=+0.80V
a. Write the cell notation indicating anode and cathode. (1)
Ans: Standard reduction potential of Ag is higher than Cu. So, Ag is a cathode and Cu is an anode.
So, cell notation is:
(-)Cu(s)/Cu++(aq.)//Ag+(aq.)/Ag(s)(+)
b. With 1M solution of the ion at 25°C and 1atm. pressure, what will be the cell potential? (1)
Solution:
Eocell = Eocathode – Eoanode
= 0.80-0.34
= 0.46 V
c. Calculate the free energy change in the reaction. (1)
Solution:
ΔGo = -nEocell
F = -2 x 0.46 x 96500 = -88,780 J
d. Can we store AgNO3 solution in a copper vessel? (1)
Ans: Cu + AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag
Here, Cu undergoes oxidation (anode) and Ag undergoes reduction (cathode). So, Eocell = Eocathode – Eoanode is positive. So, the reaction occurs spontaneously. Hence, we can’t store AgNO3 solution in copper vessels.
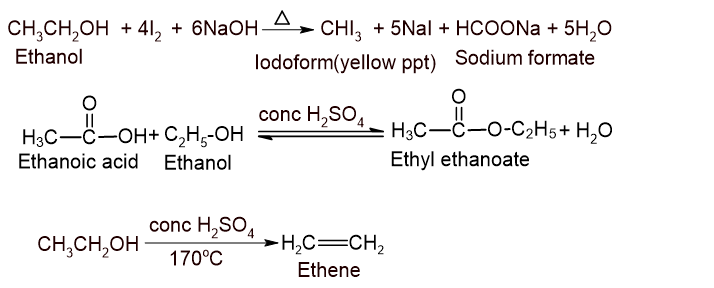
10. (A) A primary alcohol with molecular wt. 46 is boiled with sodium hydroxide and iodine. When the same alcohol is heated with ethanoic acid in presence of conc. H2SO4, one of the derivatives of the carboxylic acid is obtained. Write the reactions involved in both conditions. What would be the product obtained when the same alcohol is heated with conc.H2SO4? How would you distinguish the above alcohol from methanol? [1+1+1+1+1=5]
Ans:
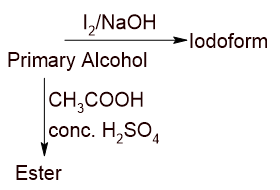
The primary alcohol is ethanol (CH3CH2OH).
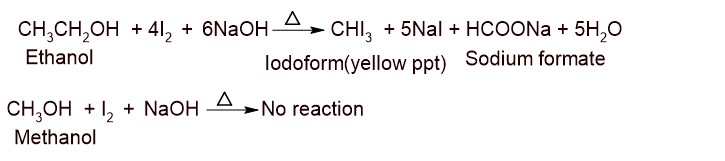
Distinction of methanol and ethanol:
Ans: Ethanol gives iodoform test whereas methanol doesnot.
(B) An aromatic compound known as oil of mirabane is prepared from benzene.
a. What product would you obtain when the compound is electrolyzed in the acidic medium? (1)
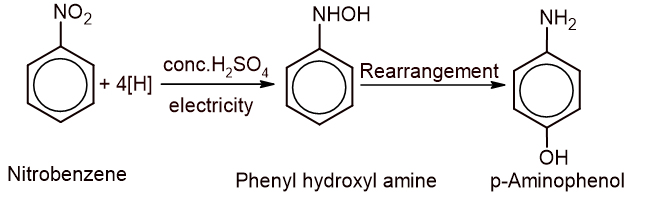
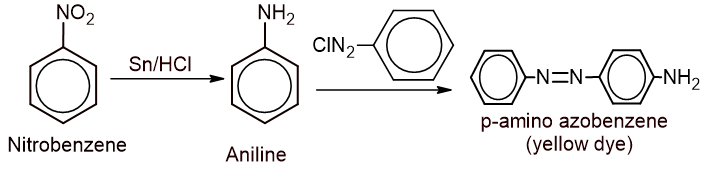
b. Give the complete reaction for the conversion of the compound into the yellow dye. (2)
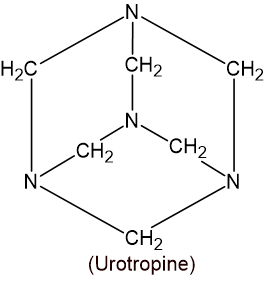
11. (A) An organic compound is used in the given figure to preserve museum specimens and also to prepare urinary antiseptics.
a. Write the reaction when the compound is heated with concentrated sodium hydroxide. (1)
HCHO+ HCHO\xrightarrow{conc.\ NaOH}\underset{\substack{sodium\\ formate}}{HCOONa}+\underset{Methanol}{CH_{3}OH}b. Draw the structure of urinary antiseptic (1)
c. Write the chemical reaction that would occur when the given preservative is treated with phenol in an acidic medium. (2)
d. How would you obtain the preservative from methanol? (1)
\underset{Methanol}{CH_{3}OH}\xrightarrow{PPC} \underset{Methanal}{HCHO}(B) A carbonyl compound with molecular formula C3H6O (it does not give silver mirror test) has treated with a compound Y which gives Z. Z on hydrolysis in acidic medium gives 2-hydroxy-2-methyl propanoic acid. Identify the carbonyl compound, Y and Z with proper reactions. [1+1+1]
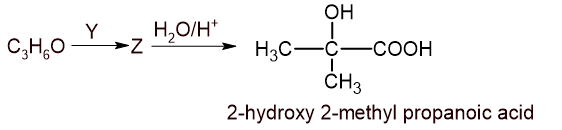
The compound that doesnot give silver mirror test is ketone. So, the carbonyl compound is propanone.
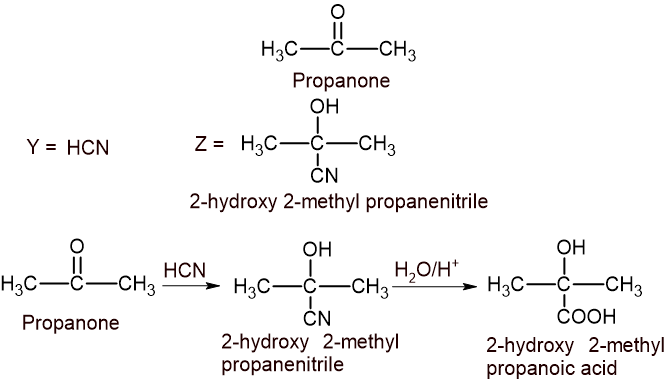
OR
(A) Starting from compound P, how do the reactions proceed ahead to obtain T which gives benzene where R is aniline? Complete the reaction sequence with suitable conditions. [5×1=5]

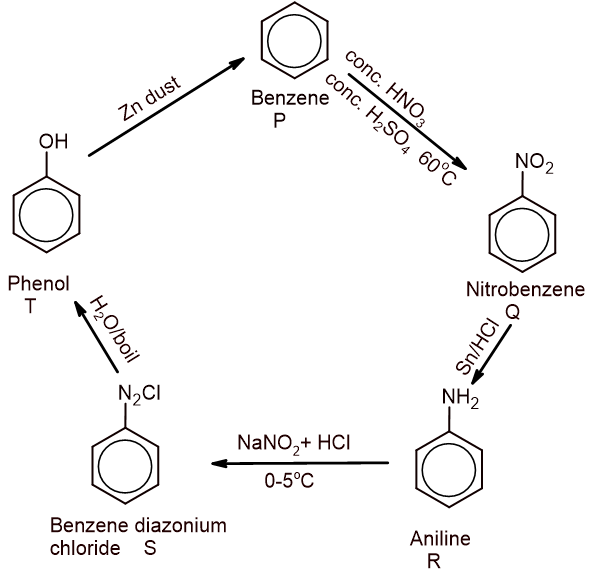
(B) Arrange the given compounds according to their ascending order of acidic strength and justify your order.
CH3CH2COOH, C6H5COOH, ClCH2CH2COOH [1+1+1]
Ans:
CH3CH2COOH<C6H5COOH<ClCH2CH2COOH
CH3CH2COOH = A
C6H5COOH = B
ClCH2CH2COOH= C
Alkyl group is an electron releasing group which decreases the acidic strength. On the other hand, acidic strength increases with an increase in the electron-withdrawing group like the benzene ring.


