Polyhaloalkane: Chloroform
Laboratory Preparation of Trichloromethane (Chloroform):
Theory:
Chloroform is prepared in the laboratory by heating ethanol or acetone with an aqueous bleaching powder paste. Bleaching powder acts as oxidizing, chlorinating, and hydrolyzing agent.
\underset{Bleaching\ powder}{CaOCl_{2}}+H_{2}O\rightarrow Ca(OH)_{2}+Cl_{2}1. From ethanol (ethyl alcohol):
i. Oxidation of ethanol into acetaldehyde:
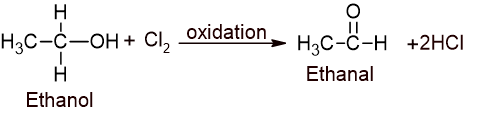
ii. Chlorination of acetaldehyde into trichloroacetaldehyde (Chloral):

iii. Hydrolysis of chloral into chloroform:
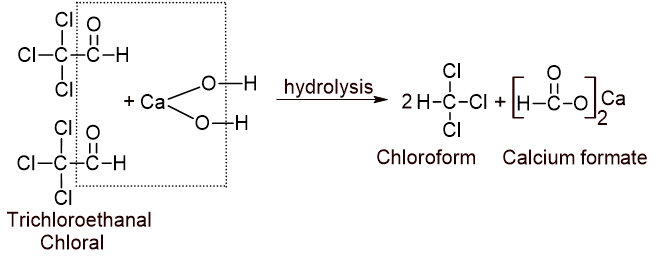
2. From acetone (Propanone):
i. Chlorination of acetone into trichloroacetone:

ii. Hydrolysis of trichloroacetone into chloroform:

Physical Properties:
- It is a colorless sweet-smelling liquid.
- It is heavier than water.
- It boils at 61 C and freezes at -63 C.
- It is insoluble in water.
- Vapour of chloroform causes unconsciousness.
Chemical Properties:
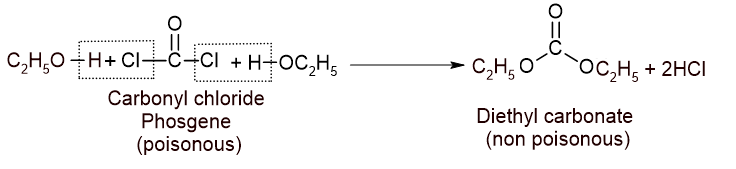
1. Action with air: Chloroform reacts with air in presence of sunlight to give carbonyl chloride or phosgene which is a highly poisonous gas.

To prevent the formation of phosgene gas:
i. It is stored in a dark bottle.
ii. Small amount of ethanol is added which converts phosgene into non-poisonous diethyl carbonate.
Test of purity of chloroform
Pure covalent contains three covalent C-Cl bonds which don’t ionize into Cl– ion. Because of the absence of Cl–, there is no reaction with AgNO3. If white ppt. is obtained with AgNO3 solution, chloroform is impure otherwise it is pure.
\begin{align*} \underset{Impure}{CHCl_{3}}+AgNO_{3}&\rightarrow \underset{White\ ppt.}{AgCl}+ HNO_{3}\\ \underset{Pure}{CHCl_{3}}+AgNO_{3}&\rightarrow No\ reaction \end{align*}2. Action with acetone: Chloroform reacts with acetone to give chloretone which is a hypnotic (sleep-inducing) drug.

3. Action with nitric acid: Chloroform reacts with concentrated nitric acid to give chloropicrin which is used as insecticides and as war gas or tear gas.
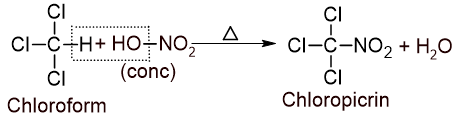
4. Action with silver: Chloroform is heated with silver powder to give acetylene gas.

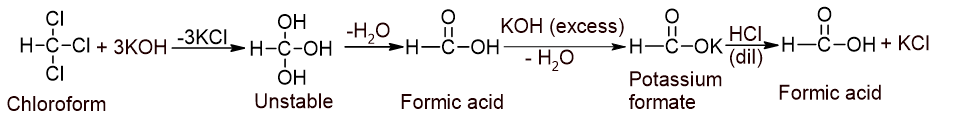
5. Action with NaOH or KOH: Chloroform is heated with aqueous KOH or NaOH followed by acidification that gives formic acid.
6. Action with phenol: Chloroform is heated with phenol in presence of aq.KOH followed by acidification gives salicylaldehyde as the major product. This reaction is called the Reimer Tiemann reaction.
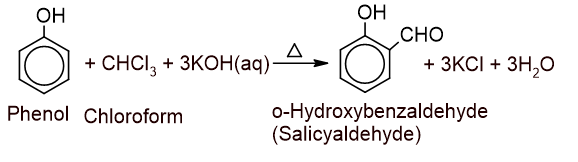
Here, p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde is formed as a minor product.
7. Action with primary amine: Chloroform is heated with primary amine in presence of alcoholic KOH to give isocyanide or carbylamine which is a bad-smelling compound. This reaction is known as carbylamine test or Isocyanide test since it is used to detect both chloroform as well as primary amine.
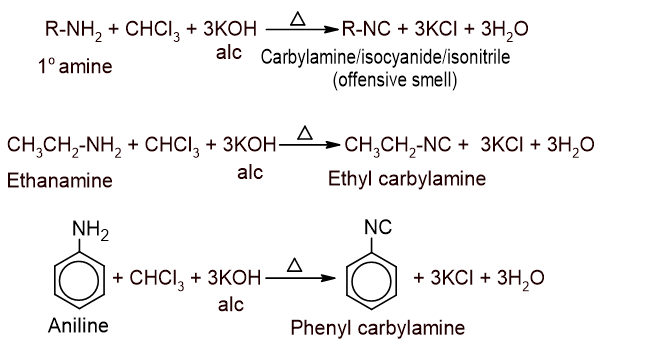
8. Reduction:
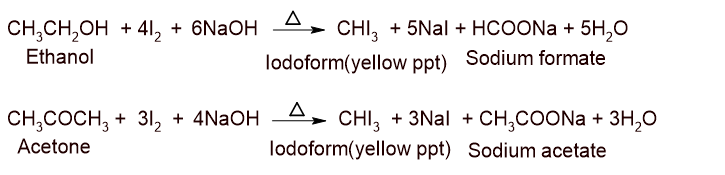
\begin{align*} \underset{Chloroform}{CHCl_{3}}+2[H]&\xrightarrow[]{Zn/HCl} \underset{Methylene\ chloride}{CH_{2}Cl_{2}}+ HCl\\ \underset{Chloroform}{CHCl_{3}}+6[H]&\xrightarrow[]{Zn/H_{2}O} \underset{Metane}{CH_{4}}+3HCl \end{align*}Iodoform test:
Alcohol containing CH3-CH-OH and aldehyde and ketone having CH3-C=O structural unit is treated with iodine and aqueous NaOH to give a compound having yellow crystalline ppt with hospital smell known as Iodoform. This test is called the iodoform test.